You Are Now Leaving the IgG4-RD Canada Website for Healthcare Professionals
The linked sites are not under the control of Amgen, and Amgen is not responsible for the content available on the linked sites. Such links do not imply Amgen's endorsement of material on any other site, and Amgen disclaims all liability with regard to your access to such linked websites. Amgen provides links to other Internet sites as a convenience to users, and access to such linked sites is at your own risk.
Do You Want to Link to Another Amgen Canada Site?
You are now leaving the IgG4-RD Canada website. Please note that these links are being provided as a convenience and for informational purposes only.




Image adopted from Lanzillotta et al9,20, Della-Torre et al17, and Maehara et al.19
- 1 Plasmablasts undergo IgG4 class switch and oligoclonal expansion, leading to increased circulating plasmablasts and IgG4.23*
- 2Plasmablasts activate CD4+ and CD8+ T cells which turn into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and cytolitic and pro-fibrotic molecules (IL-1β, IL-6, TGFβ, IFNγ).9,20,22
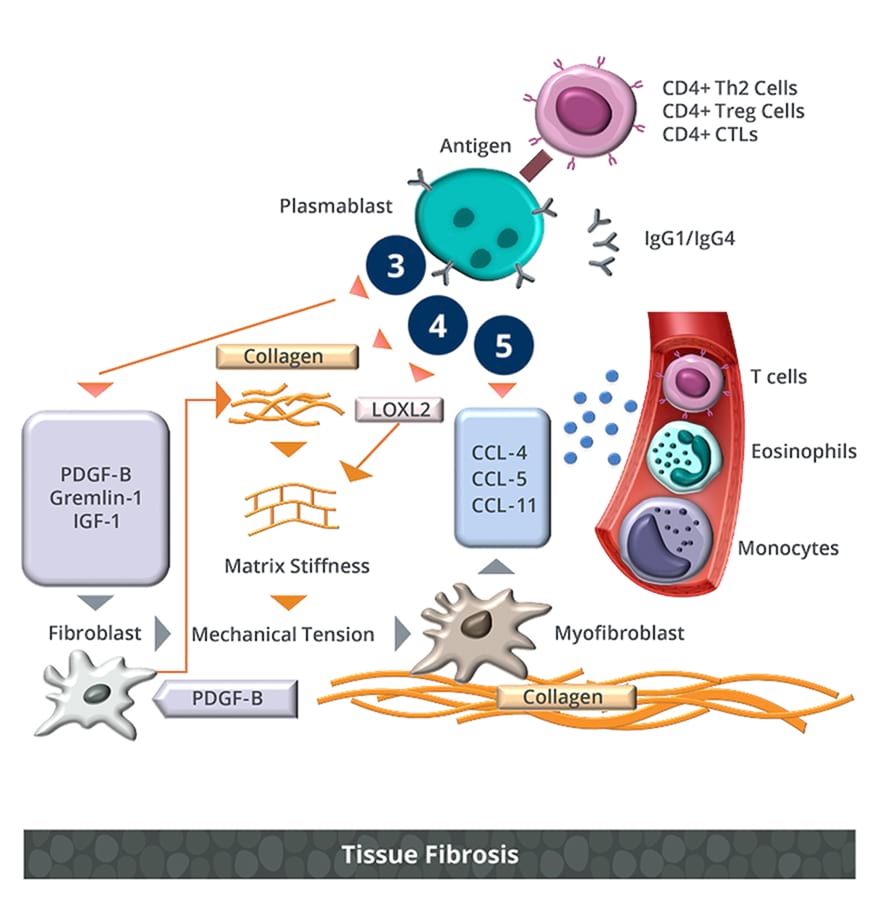

- 3 Plasmablasts secrete collagenous proteins and molecules that stimulate fibroblasts into secreting collagen.19
- 4Plasmablasts secrete enzymes that crosslink collagen molecules, regulating extracellular matrix stiffness.19
- 5Plasmablasts secrete chemokines, attracting inflammatory cells (e.g., CD4+ CTLs, eosinophils, and M2 macrophages) and further stimulating fibroblasts to secrete these chemokines.19
B-cells that drive IgG4-RD express specific cell markers, including CD197
-
CD19 in IgG4-RD
CD19 Is Expressed Widely Across the B-Cell Lineage24
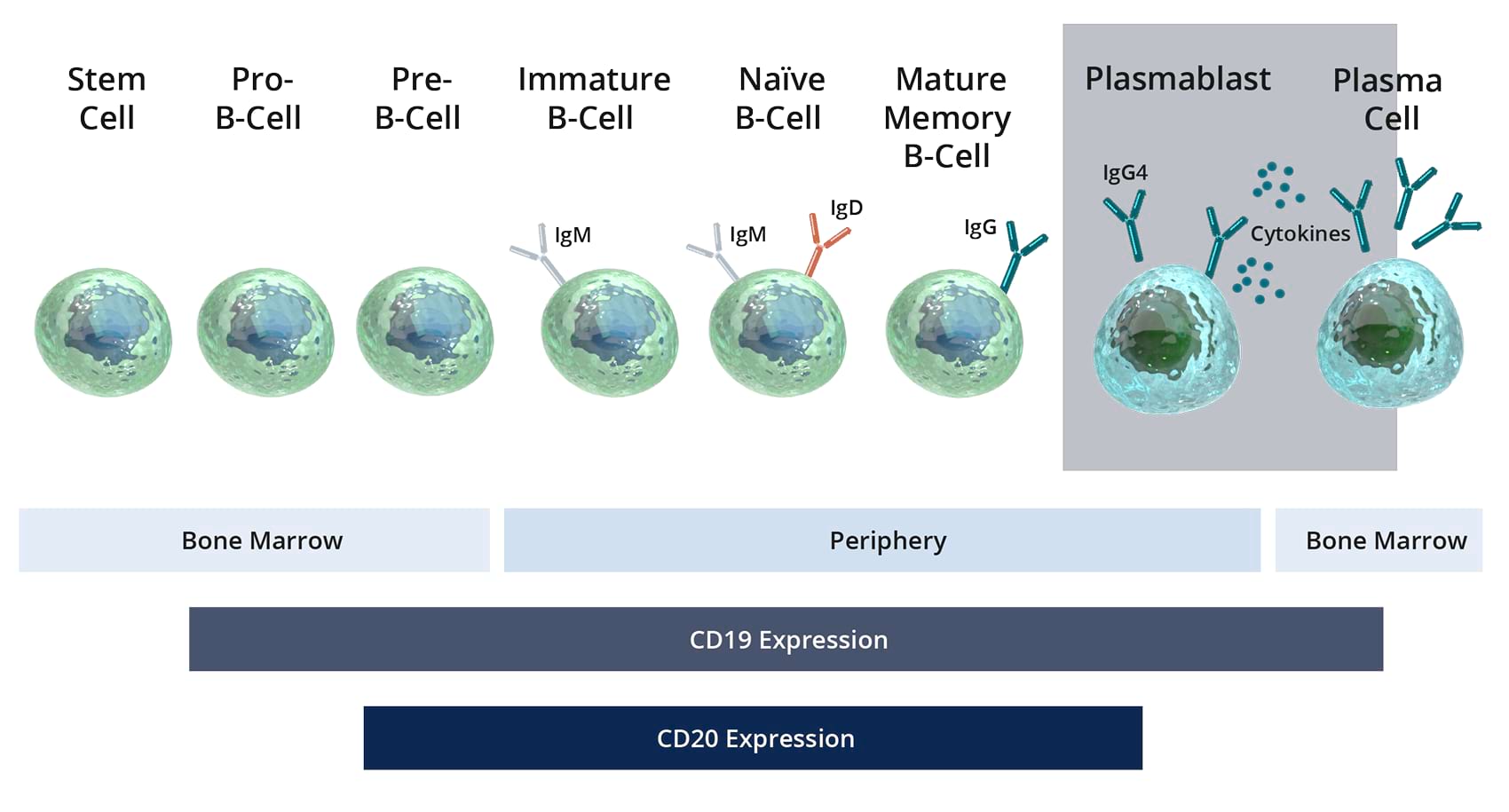

CD19+ plasmablasts and plasma cell levels increase during IgG4-RD flares.
CD, cluster of differentiation; IgD, immunoglobulin D; IgM, immunoglobulin M; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgG4, immunoglobulin 4; IgG4-RD, immunoglobulin G4–related disease.
Over time, IgG4-RD-driven inflammation and progressive fibrosis can lead to organ dysfunction and failure—early recognition of disease manifestation and intervention are key to preventing irreversible damage.6
* 60–70% of patients with IgG4-RD have elevated serum IgG4.
CCL, CC chemokine ligand; CD, cluster of differentiation; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Ig, immunoglobulin; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IFN, interferon; IgG1, immunoglobulin 1; IgG4-RD, immunoglobulin 4; IgG4-RD, immunoglobulin G4–related disease; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; LOXL2, lysyl oxidase-like 2; PDGF-B, platelet-derived growth factor B; Th2, T helper 2; Treg, regulatory T cell. IgG4, immunoglobulin 4; TGF, transforming growth factor.
-
References:
- Stone JH, et al. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(6):539-551.
- Perugino CA, et al. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(12):702-714.
- Martin-Nares E, et al. IgG4-Related Disease: Mimickers and Diagnostic Pitfalls. J Clin Rheumatol. 2022;28(2):e596-e604.
- Wallace ZS, et al. IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical and Laboratory Features in One Hundred Twenty-Five Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2466-2475.
- Lee HW, et al. Relapse rate and predictors of relapse in a large single center cohort of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis: long-term follow-up results after steroid therapy with short-duration maintenance treatment. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53(8):967-977.
- Zhang W, et al. Management of IgG4-related disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1(1):e55-e65.
- Lin W, et al. Circulating plasmablasts/plasma cells: a potential biomarker for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):25.
- Zongfei J, et al. Clinical and pathological predictors of relapse in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):106.
- Lanzillotta M, et al. Advances in the diagnosis and management of IgG4 related disease. BMJ. 2020;369:m1067.
- Rare Disease Advisor. IgG4-Related Disease: Epidemiology. Haymarkey Media. 2025. Available at: https://www.rarediseaseadvisor.com/disease-info-pages/immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-epidemiology/. Retrieved 27 January, 2025.
- Floreani A, et al. IgG4-related disease: Changing epidemiology and new thoughts on a multisystem disease. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100074.
- Rare Disease Advisor. IgG4-Related Disease Etiology. Haymarket Media. 2025. Available at: https://www.rarediseaseadvisor.com/disease-info-pages/immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-etiology/. Retrieved 15 January, 2025.
- Maritati F, et al. IgG4-related disease: a clinical perspective. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(Suppl 3):iii123-iii131.
- De Buy Wenniger LJ, et al. Exposure to occupational antigens might predispose to IgG4-related disease. Hepatology. 2014;60(4):1453-1454.
- Grasso C, et al. A Review on The Role of Environmental Exposures in IgG4-Related Diseases. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2023;10(3):303-311.
- Tsuji Y, et al. Identification of risk factors for elevated serum IgG4 levels in subjects in a large-scale health checkup cohort study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1124417.
- Karadeniz H, et al. IgG4-related disease: a contemporary review. Turk J Med Sci. 2020;50(SI-2):1616-1631.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease. Clin Chest Med. 2019;40(3):583-597.
- Della-Torre E, et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(3):968-981 e914.
- Lanzillotta M, et al. B-Cell depletion therapy in IgG4-related disease: State of the art and future perspectives. Mod Rheumatol. 2023;33(2):258-265.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Current and future advances in practice: IgG4-related disease. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024;8(2):rkae020.
- Maehara T, et al. Review of a novel disease entity, immunoglobulin G4-related disease. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;46(1):3-11.
- Baker MC, et al. The Positive Predictive Value of a Very High Serum IgG4 Concentration for the Diagnosis of IgG4-Related Disease. J Rheumatol. 2023;50(3):408-412.
- Forsthuber TG, et al. B cell-based therapies in CNS autoimmunity: differentiating CD19 and CD20 as therapeutic targets. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2018;11:1756286418761697.
- Khosroshahi A, et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688-1699.
- Baptista B, et al. Neurological Manifestations of IgG4-Related Disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017;19(4):14.
- Merck Manual. IgG4-Related Disease. Merck & Co, Inc. 2024. Available at: https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-ca/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/igg4-related-disease/igg4-related-disease#Diagnosis_v46259151. Retrieved 12 March, 2025.
- Cheuk W, et al. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related disease: an underdiagnosed and overdiagnosed entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4):226-234.
- Chen LYC, et al. IgG4-related disease: what a hematologist needs to know. Haematologica. 2019;104(3):444-455.
- Pinheiro FAG, et al. IgG4-related disease-rare but you should not forget it. Adv Rheumatol. 2024;64(1):35.
- Peng L, et al. The development and initial validation of IgG4-related disease damage index: a consensus report from Chinese IgG4-RD Consortium. RMD Open. 2024;10(1).
- Rare Disease Advisor. IgG4-Related Disease Signs and Symptoms. Haymarket Media. 2024. Available at: https://www.rarediseaseadvisor.com/hcp-resource/immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-signs-symptoms/. Retrieved 25 January, 2025.
- Wu S, et al. IgG4-related digestive diseases: diagnosis and treatment. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1278332.
- Culver EL, et al. IgG4-related hepatobiliary disease: an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(10):601-612.
- Miyabe K, et al. Gastrointestinal and Extra-Intestinal Manifestations of IgG4-Related Disease. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):990-1003 e1001.
- Cortazar FB, et al. IgG4-related disease and the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(10):599-609.
- Seo N, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-Related Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Pictorial Review of the Imaging Spectrum, Mimickers, and Clinicopathological Characteristics. Korean J Radiol. 2015;16(5):1056-1067.
- Rare Disease Advisor. IgG4-Related Disease Clinical Presentations. Haymarket Media. 2025. Available at: https://www.rarediseaseadvisor.com/hcp-resource/immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-clinical-features/. Retrieved 15 January, 2025.
- Hess AO, et al. Sinonasal IgG4-related sclerosing disease: A rare entity and challenging diagnosis. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022;7(6):1725-1732.
- Sapir A, et al. Otologic Manifestations of IgG4-Related Disease: Literature Review and Report of Two Cases. Appl. Sci. 2022;12(8353).
- Bertolini M, et al. Are there atypical sites of IgG4 related disease in head and neck region? Personal experience and literature review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025.
- Della-Torre E, et al. IgG4-related midline destructive lesion. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1434-1436.
- T. P. Afra, et al. IgG4-related skin diseases: A brief review. Journal of Skin and Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 2020;2(2):94-98.
- Katz G, et al. Clinical Perspectives on IgG4-Related Disease and Its Classification. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:545-562.
- Sangoi AR, et al. IgG4-Related Prostatitis: A Potentially Underappreciated Finding for Pathologists. Int J Surg Pathol. 2024;32(1):100-103.
- Merck Manual. Prostatitis. 2022. Available at: https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-ca/professional/genitourinary-disorders/benign-prostate-disease/prostatitis. Retrieved 27 January, 2025.
- Yamada K, et al. New clues to the nature of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a retrospective Japanese multicenter study of baseline clinical features of 334 cases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):262.
- Goodchild G, et al. Experience from the first UK inter-regional specialist multidisciplinary meeting in the diagnosis and management of IgG4-related disease. Clin Med (Lond). 2020;20(3):e32-e39.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Predictors of disease relapse in IgG4-related disease following rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(6):1000-1008.
- Tanaka Y, et al. Perspectives on current and emerging therapies for immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2023;33(2):229-236.
- Zifan Yue, et al. Risk factors for IgG4-related disease relapse: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 2022;96(3).
- Ding H, et al. Clinical patterns and risk factors for multiorgan involvement in IgG4-Related disease patients. Heliyon. 2024;10(1):e23433.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of IgG4-related disease in the USA: a claims-based analysis of commercially insured adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(7):957-962.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Assessment of patient-reported symptoms and distress in IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD): Development, clinical validation, and content validation of the IgG4-RD Symptom Severity Index. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023;63:152253.
- Chen Y, et al. Update on classification, diagnosis, and management of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(4):381-392.
- Institute for Patient Access. In Their Own Voices: The Lived Experiences of IgG4-RD Patients: Institute for Patient Access; September 21. 2022.
- Plichta DR, et al. Congruent microbiome signatures in fibrosis-prone autoimmune diseases: IgG4-related disease and systemic sclerosis. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):35.
- Umehara H, et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(3):529-533.
- Wallace ZS, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(1):7-19.
- Wallace ZS, et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: an analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3):406-412.
- Lanzillotta M, et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease reflect different prognostic outcomes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(9):2435-2442.



